optical rotation polarimeter in rate of reaction|schematic diagram of polarimeter : trading In an instrument called a polarimeter, optical rotation is measured. A linear association occurs between the rotation observed and the optically active . WEBAo Vivo - SporTV
{plog:ftitle_list}
Welcome to DigitalMZX! MegaZeux is a game creation system originally released in 1994 and still being developed today. At DigitalMZX you'll find an enormous collection of .
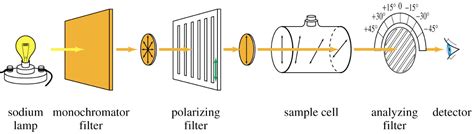
An analyzer is the component of a polarimeter that allows the angle of rotation of plane-polarized light to be determined. Specific rotations are normally measured at 20°C, and this property may be indicated by the symbol \([\alpha]^{20}_{D}\). Figure 5.4c Measurement of Optical Rotation with Polarimeter. Since the measurement results vary with the wavelength of the light being used, the specific light from a sodium atomic spectrum with the wavelength of 589 .In an instrument called a polarimeter, optical rotation is measured. A linear association occurs between the rotation observed and the optically active .The hydrolysis of sucrose by the enzyme invertase was followed by measuring the initial rate of change in polarimeter (optical rotation) readings at various initial concentrations of sucrose. The following data were obtained. . The rate .
The rate of the reaction in which sucrose is hydrolyzed to glucose and fructose is determined by observing the change in the optical rotation of sucrose as the reaction proceeds.The hydrolysis of sucrose by the enzymne invertase was followed by measuring the initial rate of change in polarimeter (optical rotation) readings, a, at various initial concentrations of sucrose. The reaction is inhibited reversibly by urea. (a) Make a plot of the data in the absence of urea and determine the Michaelis constant KM for this .PDF | On Jan 1, 2020, Shaofen Yu and others published Thermodynamic Study on the Experiment of Measuring the Rate Constant of Sucrose Hydrolysis Reaction by Optical Rotation Method | Find, read .Polarimeters can be used in kinetics experiments to follow the change in concentration of an optically active sample as a reaction proceeds. Sugars are common examples of optically active compounds. Sucrose is a disaccharide that can be broken down into its two substituent monosaccharides, glucose and fructose. This process occurs too slowly in water to be .
Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): The effect of path length on optical rotation. The longer the path of light through a solution of molecules, the more molecules will be encountered by the light, and the greater the optical rotation. The value of the optical rotation must be corrected for the length of the cell used to hold the sample.The value of the optical rotation must be corrected for the length of the cell used to hold the sample. In summary: \[[\alpha] = \frac{\alpha}{c \times l} \nonumber\] a is the measured optical rotation. c is the sample concentration in grams per deciliter (1 dL = 10 mL). That is, c = m / V (m = mass in g, V = volume in dL). l is the cell length .A polarimeter [1] is a scientific instrument used to measure optical rotation: the angle of rotation caused by passing linearly polarized light through an optically active substance. [ 2 ] Some chemical substances are optically active, and linearly polarized (uni-directional) light will rotate either to the left (counter-clockwise) or right .The optical rotation of sucrose containing solution in presence of dil. HCl at various intervals is given below 10 20 Time (minutes) Rotation (degree) 32.4 28.2 24.38 - 14.1 The value of rate constant for hydrolysis of sucrose is (1) 0.007890 min-1 .
why polarimeter is used
For a reaction A B + C. it was found that at the end of 10 minutes from the start the total optical rotation of the system was 50 o and when the reaction is complete, it was 100 o C.Assuming that only B and C are optically active and dextrorotatory. Calculate the .
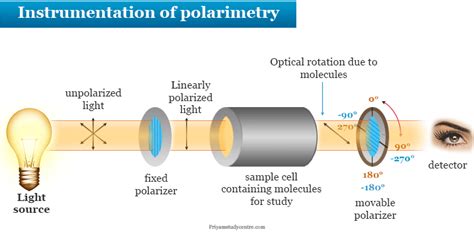
The plane of polarization can be determined by an instrument called a polarimeter, shown in the diagram below. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Operating principle of an optical polarimeter. 1. Light source 2. Unpolarized light 3. Linear polarizer 4. Linearly polarized light 5. Sample tube containing molecules under study 6. Optical rotation due to . Specific Optical Rotation Optical rotation is determined using a polarimeters The general equation for Specific Optical Rotation; [α] = specific rotation at wavelength λ T = temperature # a = Observed rotation in degrees (°) l = path length (dm) C = concentration of the analyte (g/100 mL) D-line of the sodium lamp at the visible wavelength .
Sucrose is hydrolyzed to glucose and fructose by the enzyme invertase, and the products have an overall different optical rotation than the reactant. The initial rate of change in a, which corresponds to the initial reaction rate, is measured at various initial concentrations of sucrose, in the absence and presence of the inhibitor urea: (35 pt .The instrument used to measure optical activity is called a polarimeter. When the same is used for measuring quality of sugar the name . polarimetry to study the reaction rate of the hydrolysis of sucrose. It was Dutch . optical rotation of compounds like .Purpose: The rate of reaction between sucrose and water catalyzed by hydrogen ion is followed . polarimeter. The reaction is C12 H22 O11 + H 2O + H + C16 H12 O6 + C 6H12 O6 + H + . in this experiment the optical rotation, α, is measured. Optical rotation is linear function of the concentration for each optically activeThe optical rotation of the solutions is measured with a polarimeter at a constant acid concentration. A description of the polarimeter and instructions for use can be found together with the equipments. For more information on setting the polarimeter and reading the rotation angle, see the Appendix. 2.1 Experimental, carrying out the measurements
which lamp used in polarimeter
Students use a polarimeter determine reaction order and rate constant of an acid-catalyzed sucrose hydrolysis reaction and an invertase-catalyzed reaction. . Measure the concentration of optically active compounds by determining the optical rotation of their solution. Support. Many lab activities can be conducted with our Wireless, PASPORT, .
E. Optical rotation polarimeter Used to monitor a reaction that is exothermic or endothermic, with a known enthalpy. 14. Consider the following reaction: N 2 O 4 (g) → 2NO 2 (g) The rate of the reaction above can be studied at constant temperature using a pressure probe. However, the data are complicated due to the presence of two gases. a.A polarimeter instrument determines the polarization direction of the light or the rotation produced by an optically active substance. In a polarimeter, the plane-polarized light is introduced to a tube containing the reacting solution, and the reaction can be followed without disturbing the system.
custom moisture meter flir
The measurement of the optical activity of a substance results in the angle of rotation – also known as the rotation value. A difference is made between the optical rotation and the specific angle of rotation. The optical rotation determines the measured value of the polarimeter, without taking specific physical influences into consideration.The optical rotation is measured through a polarimeter. The optical activity of optically active substances is studied by the polarimeter. Polarimetry Gives the measurement of rotation of plane-polarized light by an optically active substance. . Optical activity is a function of time and it is used to determine kinetic reactions. The optical .
E. Optical rotation polarimeter Used to monitor a reaction that is exothermic or endothermic, with a known enthalpy. 14. Consider the following reaction: N 2 O 4 (g) → 2NO 2 (g) The rate of the reaction above can be studied at constant temperature using a pressure probe. However, the data are complicated due to the presence of two gases. a.directly proportional to the length of the polarimeter tube only; . Rate constant of the reaction . The observed rotation of the mixture after 20 min was 5° while after completion of the reaction it was – 20°. If optical rotation per molar concentration of A, B and C are 60°, 40° and – 80° respectively and observed rotation of a .The rate of hydrolysis or ‘inversion’ of sucrose, by polarimetry. Aim: Determination of the rate at which sucrose hydrolyses by calculating its angle of optical rotation using a polarimeter at 25°C in 15 minute intervals for a period of ±100 minutes. Flow Chart: Results: Temperature: 25 oC___ Length of polarimeter tube: 10 cm_____
For this work, the polarimeter of Perkin-Elmer Model 141 with a Sodium lamp of 584 nm wavelength (D-line) and fitted with a digital counter was used to calculate the amount of degrees of rotation of the plane-polarised light at room temperature by 8.3 percent concentration of each L-, D-and DL-alanine solution.Optical Rotation with a Novel Polarimeter . The reaction rate equation at temperature is therefore r = – d [Su] / dt = k [H+]2 [Su] in which k = f ( only) Determination of the Reaction Rate Constant k. A natural exponential regression applied to the data set shown in Figure 6 yields the following relationship θ = (θo – θ∞) exp (–k .The basics of noninvasive methods. Artur Rydosz, in Diabetes Without Needles, 2022. 3.4.2 Polarimetry. Polarimetry, also known as stereochemistry, was developed in the 19th century as a novel analytical method for glucose concentration monitoring during industrial sugar production processes [85].Because the specific features of glucose have been observed within this .
what does a polarimeter measure
schematic diagram of polarimeter
optical rotation vs specific
how to calculate optical rotation
Resultado da This Client works best with newer browsers and faster Internet connections. Standard is recommended when Internet connections are slow, when using older browsers, or for easier accessibility. Mobile is recommended for mobile devices. To set Default to be your preferred client type, change .
optical rotation polarimeter in rate of reaction|schematic diagram of polarimeter